The Programmable SMS Gateway
Selenium SMS is designed to make it easy for software applications to send and receive SMS messages. Selenium SMS sits in between applications and the mobile networks and their messaging servers (known as “SMSCs”). Applications are provided with easy to use interfaces by which messages can be submitted or received and on the other side, Selenium SMS takes care of the complexities and technical challenges of interfacing with the mobile networks.
Download our Selenium SMS overview presentation here
Architecture
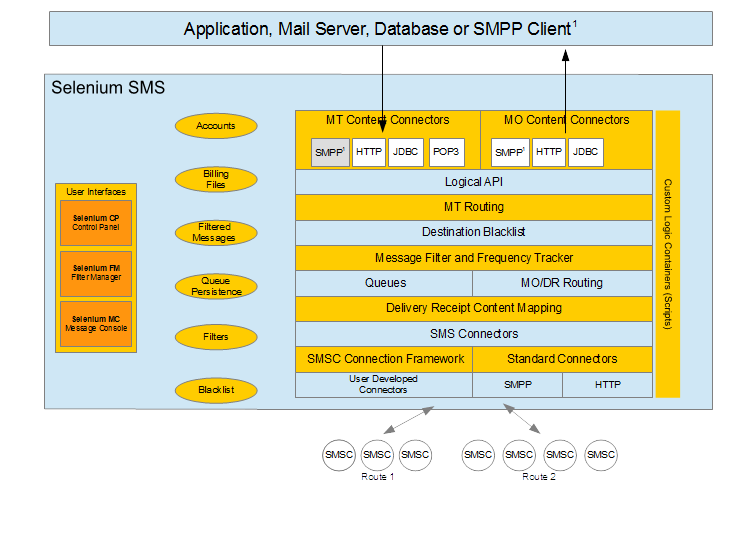
SMPP server support as shown at the top of the diagram requires a licence for the separate product Selenium SMPP Access. Connecting to downstream SMSCs with SMPP as shown at the bottom of the diagram is a standard feature of Selenium SMS.
User Interfaces
Selenium CP (Control Panel) is a web based user interface which allows operators of Selenium SMS to monitor and manage their Selenium SMS server and to make configuration changes of various sorts.
Selenium FM (Filtering Manager) is a web based user interface which allows operators of Selenium SMS to maintain message filter and frequency tracking rules and to manage messages blocked by these rules and placed in the “held messages” queue.
Selenium MC (Message Console) is a web based user interface which allows SMS messages to be sent or received. The UI design resembles that of a familiar, web based email system. user accounts may be defined so that it can be used in combination with pre-pay accounting capabilities.
Features
| MT message submission | Applications may submit MT (mobile terminated) messages using any combination of HTTP, a database such as MySQL or email via one or more POP3 enabled email accounts. If you also purchase the Selenium SMPP Access product, you can utilise SMPP to submit messages from your applications as well. |
| MO messages and delivery receipts | Applications may receive MO (mobile originated) messages and delivery receipts using any combination of HTTP, a database such as MySQL or, if you also purchase the Selenium SMPP Access product, via SMPP. |
| Standard SMSC connectivity | Selenium SMS can connect to SMSCs (Short Message Service Centres) and other SMS gateways using any of SMPP, a highly configurable HTTP connector or to the Esendex messaging service via their web services interface. |
| Accounts | The system may be used with or without the concept of a customer account. Where accounts are in use, they may be used in authentication of client applications, for authorising access to particular interfaces or for accounting purposes such as to support pre-pay service offerings. |
| MT Routing | MT messages submitted by applications need to be routed to an appropriate SMSC. Selenium SMS may be connected to many SMSCs simultaneously. These SMSC connections may be grouped into collections known as a “route”. Via the Selenium CP user interface (see below), it is then possible to define routing rules which revolve around the country code (the first so many digits) of the address to which a message is sent. |
| MO Routing | MO messages and delivery receipts received from the mobile networks must be routed to an appropriate application. Selenium SMS can perform this routing based on configuration rules of various sorts. The routing decisions relating to delivery receipts is largely automatic and made with reference to details of the MT message to which the delivery receipt relates. |
| Blacklist | Block messages sent to particular destination addresses |
| Filtering | You may need to filter messages which contain inappropriate content in order that you comply with the rules imposed by your “downstream” mobile network operators. Selenium SMS allows you to define message filtering rules which applied to MT messages submitted by applications. In the event that a message matches a rule, it is “held” in a database queue and this queue can be managed via the Selenium FM user interface. Managing the queue involves inspection of the messages it contains and deciding to either let the message through to the mobile network or to block it permanently. |
| Frequency Tracking | Selenium SMS is able to monitor message senders for suspcious patterns of behaviour such as the submission of large numbers of messages from the same source address to the same destination address. Such behaviour may be indicative of “spam”. Selenium FM provides you with the ability to specify rules which Selenium SMS will evaluate and enforce at run-time as it tracks message submission frequency from different senders to different destinations. Messages blocked due to “frequency violations” are also placed in the Selenium FM held messages queue and may be subject to similar management actions as for messages blocked by the message filtering sub-system. |
| Delivery receipt content mapping | If your Selenium SMS instance is connected to multiple downstream networks over SMPP, it may be the case that these different networks produce their delivery receipts according to differing content standards, for example with different error codes or descriptions. Via the Selenium CP user interface, users of Selenium SMS may specify rules which allow the standardisation of delivery receipt content to take place at run-time. |
| Billing | Selenium SMS is able to produce audit records, often referred to as CDRs (Call Data Records) at various points in the message processing lifecycle. These records contain data which has been selected to support typical billing and support scenarios. |
| Operational Monitoring and Management | Selenium SMS includes a user interface called Selenium CP. “CP” provides up to date statistical information about messages handled by the system and at a glance depiction of the “health” of each key system component such as each of the connections to SMSCs. It also provides importent information such as graphs which depict the “latency” of each SMSC connection so that performance issues can be analysed and informed discussions with SMSC oeprators can take place supported by concrete, unarguable data about connection performance. The status of various components may also be changed via CP. For example, connections may be taken off line or brought back on line at the click of a mouse. Finally, the system may be configured to send alerts by email in response to the occurrence of system issues. |
| Configuration | The most important system configuration details may be updated via Selenium CP without the need to restart the Selenium SMS server. A special “configuration service” in Selenium SMS handles all configuration change requests issued via Selenium CP one at a time to ensure that such changes are handled in a steady, measured way, which should not be allowed to disrupt the flow of messages. |
| Programmability | Selenium SMS allows the operator to use standard JavaScript to process MT and MO messages (including delivery receipts) at run-time. This is an immensely powerful capability, allowing highly customised logic to be applied to message processing. Message content may be modified by scripts and messages may be rejected or rerouted. |
| Custom SMSC connectivity | Should you need to connect Selenium SMS to an SMSC whose interface is not supported as standard, the product includes the “SMSC Connection Framework”. This allows Java developers to create additional connector types and to add them to the configuration of Selenium SMS, thus allowing Selenium SMS to interact with the SMSC. |
Purchasing
Prices are available on application to Selenium Software. Note that Selenium SMS may be purchased with full source code and developer training if required.




